- Pharmacology
- Allergy, Immunology, and ENT
- Cardiology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Adolescent Medicine
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Diseases
- Neurology
- OB/GYN
- Practice Improvement
- Gynecology
- Respiratory
- Dermatology
- Mental, Behavioral and Development Health
- Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Sexual Health
- Pain
Asymptomatic Papular Rash in Infant With Rhinorrhea
A 10-month-old boy with an asymptomatic rash is brought to your office by his mother. The rash, which began on the legs and spread to the arms, face, and buttocks, has been present for 3 days. Other than rhinorrhea and nasal congestion for the past 3 to 5 days, the infant has been well, although fussier than usual, especially at night. His appetite is normal. The rash has persisted despite the application of bacitracin, petroleum jelly, and cortisone. He has had no sick contacts with a similar rash or illness. His immunizations are up-to-date.
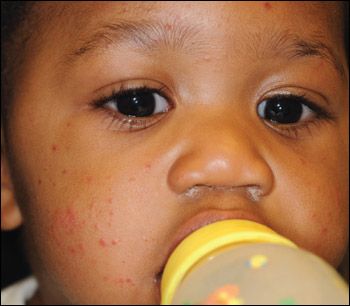
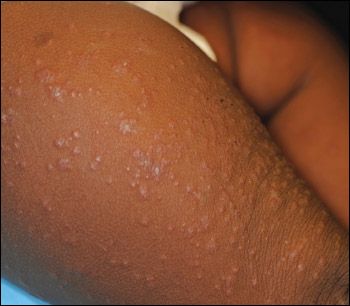
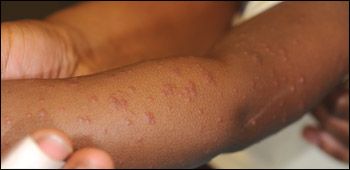
THE CASE: A 10-month-old boy with an asymptomatic rash is brought to your office by his mother. The rash, which began on the legs and spread to the arms, face, and buttocks, has been present for 3 days. Other than rhinorrhea and nasal congestion for the past 3 to 5 days, the infant has been well, although fussier than usual, especially at night. His appetite is normal. The rash has persisted despite the application of bacitracin, petroleum jelly, and cortisone. He has had no sick contacts with a similar rash or illness. His immunizations are up-to-date.
The infant is active, playful, and happy. Symmetrically distributed, edematous, monomorphic, erythematous papules of 2 to 3 mm are noted on the face, ears, hands, feet, and buttocks and on the extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. The infant also has mild anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Remaining physical findings are normal.
Answer and Discussion on Next Page
Answer: Gianotti-Crosti syndrome
DISCUSSION: This infant has Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis of childhood, first described by Fernando Gianotti1 in 1955. This disorder primarily affects children younger than 5 years but can occur in adolescents and adults. A family history of atopy may be present, although a personal or family history of atopy does not increase the incidence of GCS.
GCS is usually associated with a viral illness. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are the most common causes. Because of routine universal hepatitis B vaccination during infancy, EBV infection is a more common cause in the United States, accounting for half to three-quarters of cases in some series.2-6 Other pathogens that cause GCS are enteroviruses, cytomegalovirus (CMV), parvovirus, parainfluenza virus, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human herpesvirus 6, HIV, poxvirus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, β-hemolytic streptococci, Bartonella henselae, and Borrelia burgdorferi. GCS is also associated with the administration of certain vaccines, including those for influenza; measles, mumps, and rubella; hepatitis B; hepatitis A; and polio (oral vaccine).
The characteristic rash of GCS consists of symmetrical monomorphous, flat-topped, pink-brown papules or papulovesicles, 1 to 10 mm, that occur on the face, buttocks, feet, and extensor aspects of forearms and legs. Other findings include malaise, low-grade fever, diarrhea, and rhinorrhea. Lymphadenopathy is present in about 30% of patients, usually in the cervical, axillary, or inguinal regions.2,7 Hepatitis, when present, is usually anicteric. Splenomegaly is uncommon.8
GCS is a clinical diagnosis. No laboratory findings are characteristic of GCS. Patients may have lymphocytosis or lymphopenia.8 Liver enzyme levels may be elevated in patients with EBV, CMV, or HBV infections. An etiological diagnosis for GCS should be pursued in patients with increased risk of hepatitis B, immunocompromised patients, and patients who have close contacts with immunocompromised persons or pregnant women.
The treatment of GCS is supportive and should include patient and parental reassurance. Topical emollients can be used for mild pruritus and topical calamine lotion for moderate pruritus. A night dose of an antihistamine (eg, diphenhydramine) can be helpful in patients with severe pruritus, although this is not a prominent feature of GCS. The rash can last from 10 days to 6 months.
Most children with GCS have an excellent prognosis. Children with darker skin may have postinflammatory hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, which can persist for several months after resolution of the rash.8 This patient's rash had resolved by his 2-week follow-up appointment with his pediatrician.
Quiz Results
Online Poll
Powered By
WebsiteGear
: Requires Javascript Enabled On Your Browser.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Erythema infectiosum, or fifth disease, like GCS, presents with a nonspecific prodromal illness and acral eruption. The rash of erythema infectiosum begins on the cheeks and spreads to the extremities, is usually macular rather than papular, and may involve the trunk. Erythema infectiosum may trigger an aplastic crisis in patients with severe hemoglobinopathies and can cause hydrops fetalis in patients who are pregnant.
Papular urticaria, or insect bite–induced hypersensitivity reaction, is characterized by recurrent eruptions of papules, vesicles, target lesions, or wheals. The lesions are symmetrical and usually are grouped in crops or clusters on exposed areas. The punctum left by the insect (eg, flea, mosquito, bedbug, or mite) after a bite may be visible. The condition may take weeks to resolve.
Cutaneous drug reactions in children are relatively common. The rash may be accompanied by fever, arthralgias, general malaise, and other systemic findings. About half of these rashes are morbiliform; fewer are urticarial, exanthematous, or eczematoid eruptions. However, almost any morphological condition can occur, including exfoliative dermatitis; bullous dermatosis (eg, epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome); petechial, acneiform, or lichenoid eruption; photodermatitis; and fixed drug eruption. Typically, after 5 to 10 days of drug therapy, red macules and papules erupt on the extremities and spread centrally to the trunk. The lesions may become confluent; conjunctival and oral mucosal erythema may be prominent.
Scabies in infants is usually widespread and commonly involves the face as well as the palms, soles, and trunk. Infants with scabies are usually fussy and have intense pruritus, which distinguishes the eruption from GCS.
References:
REFERENCES:
1.
Gianotti F. Report on a special case of toxic infection characterized by a desquamative erythemato-infiltrative eruption with lenticular foci and a selective localization at the extremities [in Italian].
Soc Ital Dermatol Sifilogr Sezioni Interprov Soc Ital Dermatol Sifilogr
. 1955;96:678-697.
2.
Taïeb A, Plantin P, Du Pasquier P, et al. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome: a study of 26 cases.
Br J Dermatol
. 1986;115:49-59.
3.
Smith KJ, Skelton H. Histopathologic features seen in Gianotti-Crosti syndrome secondary to Epstein-Barr virus.
J Am Acad Dermatol
. 2000;43:1076-1079.
4.
Maeda S, Tsuda H, Haruki S, Mitsuto I. Atypical Epstein-Barr virus infection associated with Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and Bell's palsy.
Pediatr Int
. 1999;41:315-317.
5.
Drago F, Crovato F, Rebora A. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome as a presenting sign of EBV-induced acute infectious mononucleosis.
Clin Exp Dermatol
. 1997;22:301-302.
6.
Hofmann B, Schuppe HC, Adams O, et al. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Pediatr Dermatol
. 1997;14:273-277.
7.
Chuh A, Lee A, Zawar V. The diagnostic criteria of Gianotti-Crosti syndrome: are they applicable to children in India?
Pediatr Dermatol
. 2004;21:542-547.
8.
Brandt O, Abeck D, Gianotti R, Burgdorf W. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome.
J Am Acad Dermatol
. 2006;54:136-145.
Young woman with tick bites presents with erythematous papules, headaches, and fatigue
April 8th 2024A young woman with no significant past medical history returns from hiking with several white-spotted ticks and experiences erythematous papules, rashes, headaches, and fatigue. What’s the diagnosis?
